x
“Natura 2000” Lower Pilica Valley
Natura 2000 is a EU-program to develop a network of protected areas. Its aim is to preserve certain types of natural habitats and species that are considered valuable, but are threatened with extinction. Two EU directives form its legal base: the Birds Directive (2009) and the Habitats Directive (1992). In Poland, the above regulations were introduced by the Act of April 16, 2004 on the Protection of Nature.
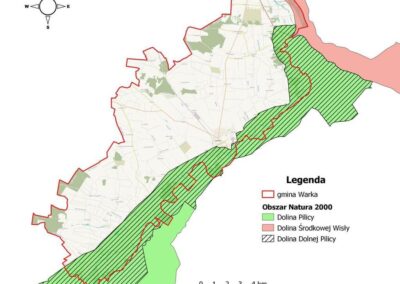
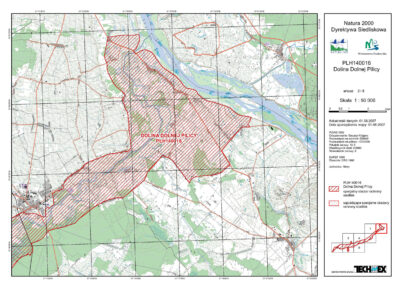
The European Commission included the Lower Pilica Valley in the program on December 12, 2008 under reference number PLH140016. The Area is mostly located in the Mazovian Province (88%), in the districts of Kozienice (Magnuszew and Grabów nad Pilicą), Białobrzegi (Stromiec, Białobrzegi, Promna, Wyśmierzyce), Przysucha (Klwów and Odrzywół), Grójec (Nowe Miasto nad Pilicą, Mogielnica, Warka), with the rest in the Łódź Province (12%) in the districts of Tomaszów and Opoczno. Warka is one of the largest towns neighboring the Area.
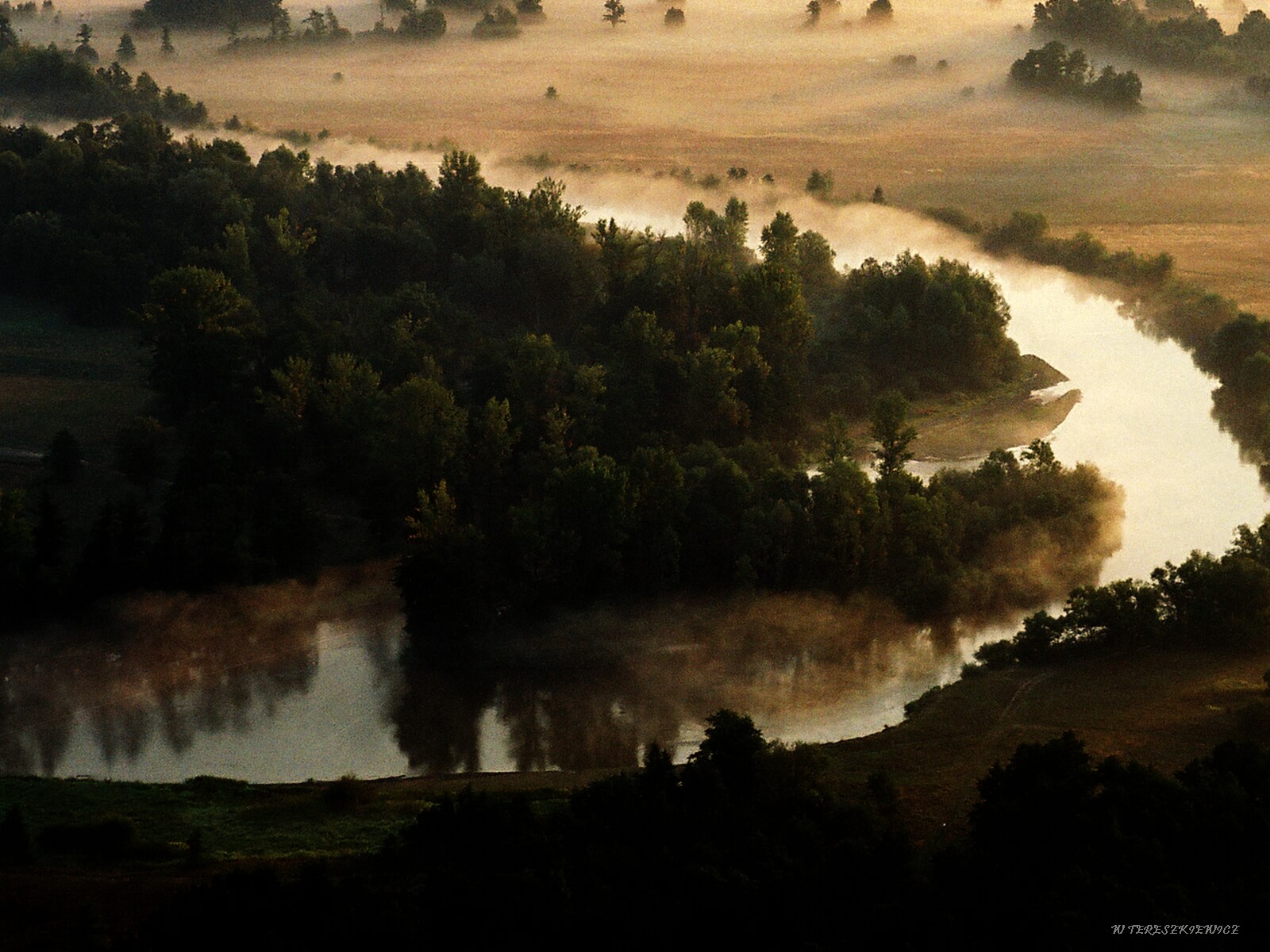
It further includes a nearly 70-mile-long section of the Pilica River Valley, which is between 0,5–6 miles wide. Its northern border is a steep escarpment with a relative height of up to 65 ft. The southern part is flat and mostly wooded. This section of the Pilica River is 330–500 ft wide, and it meanders strongly, forming numerous islands, shoals, and sand banks. The lands that tend to flood have been partially reclaimed. There is a strong presence of meadows and pastures with varying degrees of moisture and clusters of sedges and reeds.
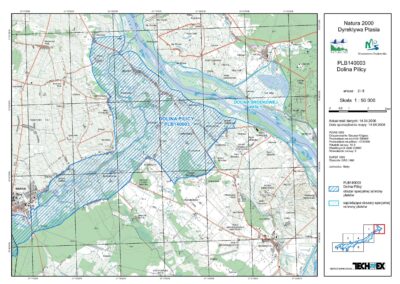
The Area strongly overlaps with the Natura 2000 Lower Pilica Valley Special Protection Area no PLB140003.
Climate
The average annual air temperature is 45.5°F, with July being the warmest month (the average air temperature is 65°C), and January being the coldest one (the average air temperature is 35.5°F). The number of days when the temperature falls below 32°C amounts to about 43 days, and the number of days with frost varies from 100 through 118.
The snow cover persists for 38–60 days. The vegetative period lasts 170–180 days. The faint precipitation, which is lower than 530 mm, is brought mainly by Atlantic humid air masses. The months with the smallest number of clouds are August and September, as opposed to December on the other end of the spectrum. In summer, the sun shines for about 9.5 hours, while in winter, the number of sunny hours amounts to 2.5. The prevailing winds are westerly and northwesterly. Southerly winds are rare.
Soil
The soil in the Area is mediocre and only at times diversified. On the northern slope and the high terrace of the Pilica River, the soil consists of loamy and dusty sands from the east, used for intensive horticulture and agriculture. In the Pilica Valley itself, there are mainly sandy alluvial soils that are light and very light in structure and cohesive muds, which are not particularly homogenous. The flood terraces are composed of alluviums and organic soils that are not unevenly moist.
The natural habitats in the Area can be categorized into:
- oxbow lakes and water reservoirs;
- meadows that vary in moisture;
- lowland and mountain meadows;
- willow, poplar, alder, and ash forests.
The animal species in the Area protected under the “Natura 2000” Program include:
- European beavers;
- European otters;
- European fire-bellied toads (amphibians);
- Amur bitterlings (fish);
- Asps (fish);
- Weaterfish (fish);
- Sabanejewia aurata (fish);
- Ramshorn snails (snail);
- Green club-tailed dragonflies (dragonfly);
- Large white-faced darters (dragonfly);
- Large coppers (butterfly).